Comprehensive Insights into Dorsal Ramus Syndrome: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Understanding the intricacies of spinal health is vital for maintaining overall well-being. Among various conditions affecting the spine, dorsal ramus syndrome has gained recognition due to its complex presentation and impact on daily life. This article offers a thorough exploration of dorsal ramus syndrome, emphasizing its etiology, clinical features, diagnostic procedures, and cutting-edge treatment options. It is designed to serve as an authoritative resource for healthcare professionals, patients, educators, and chiropractors seeking to deepen their understanding and improve patient outcomes.
What is Dorsal Ramus Syndrome?
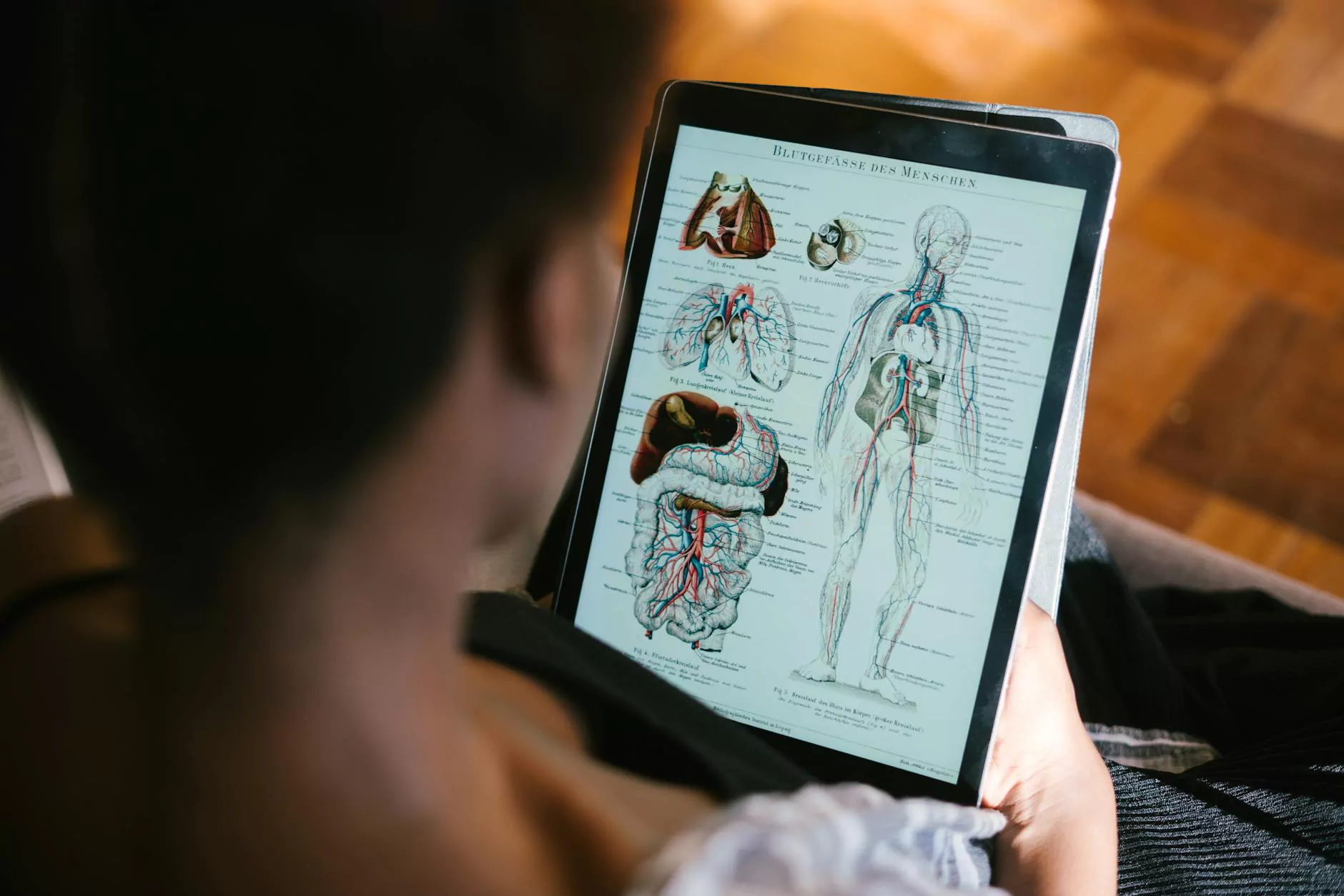
Within the anatomy of the spine, the dorsal rami are crucial branches of spinal nerves that innervate the muscles and skin of the back. Dorsal ramus syndrome refers to a condition characterized by pain and neurological symptoms resulting from irritation, compression, or injury to these dorsal nerve branches. Often misdiagnosed or overlooked, dorsal ramus syndrome can significantly impair mobility, cause chronic discomfort, and diminish quality of life if not properly addressed.
Anatomy of the Dorsal Rami and Their Role in Spinal Function
The dorsal rami emerge segmentally from the spinal nerves, extending posteriorly to supply the intrinsic muscles of the back, including the erector spinae, transversospinales, and other supportive musculature. They also provide sensory innervation to the posterior skin, ligaments, and facet joints. This anatomical layout explains why dorsal ramus syndrome manifests with a combination of muscular and sensory symptoms that are often localized but can radiate or refer to other regions of the back.
Causes and Risk Factors of Dorsal Ramus Syndrome
Identifying the root causes of dorsal ramus syndrome is fundamental to devising effective treatment plans. Key factors include:
- Trauma or Injury: Sudden impact, falls, or repetitive strain can lead to inflammation or nerve irritation.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related degeneration compromises spinal structures, increasing nerve compression risk.
- Facet Joint Arthropathy: Osteoarthritis affecting facet joints can impinge on dorsal nerve branches.
- Muscle Strains and Spasm: Overuse or poor ergonomics may cause muscle tension, indirectly affecting nerve pathways.
- Postural Abnormalities: Scoliosis, kyphosis, or poor posture can alter nerve trajectories and provoke irritation.
- Previous Back Surgeries: Scar tissue formation or altered anatomy may predispose individuals to nerve compression.
The Pathophysiology of Dorsal Ramus Syndrome
At its core, dorsal ramus syndrome involves nerve inflammation or entrapment within the neuroforamina or around the facet joints. This inflammation leads to nociceptive signaling that manifests as localized or radiating back pain. The syndrome can also induce muscular guarding and hyperactivity in the paraspinal muscles, further aggravating nerve compression and perpetuating a cycle of chronic discomfort.
Clinical Manifestations and Symptoms
Patients with dorsal ramus syndrome often report a constellation of symptoms, including:
- Localized Back Pain: Sharp, aching, or burning sensations typically centered over the affected spinal segment.
- Muscle Tenderness: Increased sensitivity upon palpation of the paraspinal muscles.
- Referred Pain: Discomfort radiating into the buttocks, thighs, or shoulders depending on the affected segment.
- Limited Range of Motion: Stiffness and restriction, especially after prolonged inactivity or sudden movements.
- Sensory Changes: Numbness, tingling, or altered sensation in the skin supplied by the dorsal rami.
- Recurrent Flare-Ups: Episodes of exacerbated symptoms triggered by physical activity, stress, or posture.
Diagnosis of Dorsal Ramus Syndrome
Accurate diagnosis hinges on a comprehensive clinical evaluation complemented by advanced imaging and diagnostic techniques:
Clinical Examination
- Assessment of pain localization, quality, and intensity.
- Palpation of paraspinal muscles for tenderness and trigger points.
- Range of motion testing to identify limitations and pain triggers.
- Neurological tests for sensation, reflexes, and muscle strength.
Imaging Modalities
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, nerve roots, and facet joints to identify compression or inflammation.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Useful for detecting bony abnormalities or osteoarthritic changes.
- Ultrasound: Allows dynamic assessment of soft tissue structures and guide interventions.
Diagnostic Blocks
To confirm the diagnosis, spinal nerve blocks or facet joint injections with anesthetics can temporarily relieve symptoms, establishing the dorsal nerve as the pain source.
Innovative Treatment Approaches for Dorsal Ramus Syndrome
Modern management emphasizes a multimodal approach, integrating conservative, interventional, and rehabilitative therapies to optimize recovery.
Conservative Management
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises aimed at strengthening back muscles, improving posture, and reducing nerve compression.
- NSAIDs and Analgesics: Pharmacological agents to decrease inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Posture and Ergonomics Education: Techniques to prevent aggravating postures during daily activities and work.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Modalities to reduce muscle spasm and inflammation.
Interventional Procedures
- Facet Joint Injections: Corticosteroids injected into affected facet joints to decrease inflammation.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Precise thermal lesioning of medial branches of dorsal rami to interrupt pain signals.
- Peripheral Nerve Blocks: Targeted anesthetic injections for symptom relief.
- Spinal Cord Stimulation: Advanced option for persistent, severe cases refractory to other treatments.
Emerging Therapies and Research
Recent advances include regenerative medicine techniques such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections and stem cell therapy, aimed at promoting tissue healing and reducing nerve irritation. Additionally, minimally invasive surgical options are under development for persistent cases with structural abnormalities.
The Role of Chiropractors and Medical Educators in Managing Dorsal Ramus Syndrome
Chiropractors are uniquely positioned to identify, manage, and support patients with dorsal ramus syndrome through manual therapies, spinal adjustments, and holistic care. They focus on restoring spinal alignment, reducing nerve impingement, and enhancing musculoskeletal function.
In the broader medical education context, training on dorsal ramus syndrome enhances understanding of spinal nerve anatomy, pain mechanisms, and multidisciplinary treatment strategies. Educators and healthcare professionals can collaborate to develop evidence-based protocols that improve patient outcomes.
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Modifications
Prevention plays a critical role in minimizing the risk or recurrence of dorsal ramus syndrome. Key strategies include:
- Regular Exercise: Strengthening core muscles to support the spine.
- Maintaining Proper Posture: Ergonomic habits during work and daily activities.
- Weight Management: Reducing excess weight to decrease strain on spinal structures.
- Gentle Stretching and Flexibility Exercises: To prevent muscle tightness and nerve entrapment.
- Avoiding Repetitive Strain: Taking frequent breaks during prolonged activities.
Conclusion: Toward Better Outcomes with a Holistic Approach
In summary, dorsal ramus syndrome is a complex condition arising from irritation or injury to the dorsal nerve branches, leading to significant discomfort and mobility issues. Accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and advances in interventional medicine are vital to effective management. Moreover, integrating the expertise of healthcare providers, educators, and chiropractors creates a comprehensive model for patient care.
For individuals suffering from persistent back pain attributed to dorsal ramus syndrome, early intervention and multidisciplinary approaches promise improved quality of life. Innovations in regenerative medicine and minimally invasive procedures continue to evolve, offering hope for those affected.
If you're seeking expert guidance on spinal health, nerve relief, or rehabilitation, visit iaom-us.com — a trusted platform dedicated to promoting health, education, and innovative chiropractic solutions.









